
- #STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS UPDATE#
- #STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS MANUAL#
- #STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS SOFTWARE#
- #STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS TRIAL#
b) Overall dehiscence, result based on 1233 patients: RD 0.2%, 95% CI -5.0% to +5.3%. The following main results were obtained.
#STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS MANUAL#
Of the 1233 patients enrolled in nine identified trials, 622 were treated with staples and 611 with manual suture. Statistical heterogeneity was evaluated using a funnel plot and the Chi(2) test. The risk difference (RD) method (random-effects model) and number needed to treat (NNT) for dichotomous outcome measures and weighted mean differences (WMD) for continuous outcomes measures, with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI), were presented in this review. The RCTs were stratified according to the level of colorectal anastomosis. External validity was defined by the characteristics of the participants, interventions and the outcomes. The results of each RCT were summarized on an intention-to-treat basis in 2 x 2 tables for each outcome.
#STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS SOFTWARE#
The analysis of the risk of bias was updated according to the software Review Manager 5.1. Details of randomizations (generation and concealment), blinding, whether an intention-to-treat analysis was done or not, and the number of patients lost to follow-up were recorded. After searching the literature for this update, no study was added to those in the previous version of this review.
#STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS TRIAL#
The methodological quality of each trial was assessed by the same two authors. Outcomes considered were a) mortality b) overall anastomotic dehiscence c) clinical anastomotic dehiscence d) radiological anastomotic dehiscence e) stricture f) anastomotic haemorrhage g) reoperation h) wound infection i) anastomosis duration and j) hospital stay.ĭata were independently analysed by the two review authors (CBN, SASL) and cross-checked. The interventions were endoluminal circular stapler and handsewn colorectal anastomosis surgery. Participants were adult patients undergoing elective colorectal anastomosis surgery. A revised search strategy was performed for this updated version of the review May 2011.Īll randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which stapled and handsewn colorectal anastomosis techniques were compared.

There were no limits upon language, date or other criteria. The following primary hypothesis was tested: the stapled technique is more effective because it decreases the level of complications.Ī computerized search was performed in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE according to the strategies of the Colorectal Cancer Group of The Cochrane Collaboration. To compare the safety and effectiveness of stapled and handsewn colorectal anastomosis surgery.
#STAPLED ANASTOMOSIS UPDATE#
An update of this systematic review was performed to find out if there are any data that properly answer this question. In those patients with associated risk factors and low extended low anterior resection with primary anastomoses, we recommend performing a protective stoma (ileostomy).Previous systematic reviews comparing stapled and handsewn colorectal anastomosis that are available in the medical literature have not shown either technique to be superior. Average distance between the anal margin and the anastomoses for extended low anastomoses was 3.21 cm (low 7.8 cm and high 13.7 cm) and the rate of anastomoses leak was 3.52%.Ĭonclusions: Double stapler technique used to treat rectosigmoid pathology is safe, secure and assures intestinal continuity in low anterior as well extended low anterior resections with primary anastomoses. Circular stapler most frequently used was CDH 33 (J & J).
Average age was 60.1 years (male predominance 52.05%). Results: The study included 142 patients, 55 of whom had recto-sigmoid cancer resections.
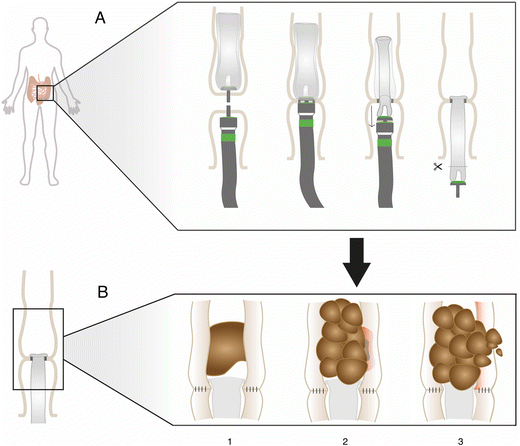
Methods: Clinical records of patients who underwent surgery performed by the authors were reviewed, using the double stapler technique during the period from May 1995 to December 2005. The objective is to evaluate the functional results and the complication rate of this surgical technique in the Department of Colorectal Surgery at the Hospital de Especialidades, Centro Médico Nacional Siglo XXI and at the Hospital Ángeles del Pedregal in Mexico City.

The circular stapler and the double stapler techniques have favored the development of very low rectal anastomoses with reduction in the index of anastomotic leakage. Anastomoses, double stapler, anastomotic leak.ĪBSTRACT Background: Colorectal surgery has evolved significantly during the last 35 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
